The slope of the line represents the per-unit variable cost, and the steeper the slope, the higher the variable cost per unit. This visualization helps in understanding the scalability of variable costs and their impact on total production costs. By comprehensively mixed cost analyzing mixed costs, businesses can identify the blend of fixed and variable components, allowing them to allocate resources efficiently. Implementing robust cost strategies ensures that organizations can control expenses and optimize performance. This understanding is essential for businesses to accurately allocate costs to the respective cost centers and budget effectively.

Managing Mixed Costs in Organizations
The commission, on the other hand, acts more like a variable cost because it’s based on the productivity of the employee. The more the employee sells the greater the sales commission expense becomes. The company can eliminate this expense altogether if it doesn’t sell anything for the month.

Applications in Business Decision-Making
- This information enables the company to make a well-informed decision about whether to proceed with the expansion.
- This is fairly easy to deal with when we are dealing with an external cost where we are given the variable rate and the fixed cost.
- A comprehensive cost analysis empowers organizations to make informed decisions, streamline operations, and adapt to changing market dynamics, ultimately driving sustainable profitability and growth.
- The fixed portion is a base charge, representing a minimum cost even with no output.
- They also get clear on how changing sales or production levels affect overall expenses, leading to smarter moves for growth and savings.
Once you know the total fixed cost, pick one point and note the total dollar and the total activity and use the formula below to calculate variable cost per activity. One of the most common mistakes in cost accounting is the misclassification of costs. Misclassifying costs as fixed, variable, or mixed can lead to significant errors in financial analysis, budgeting, and decision-making. This misclassification often stems from a lack of understanding of how costs behave or from oversimplifying the cost structure.
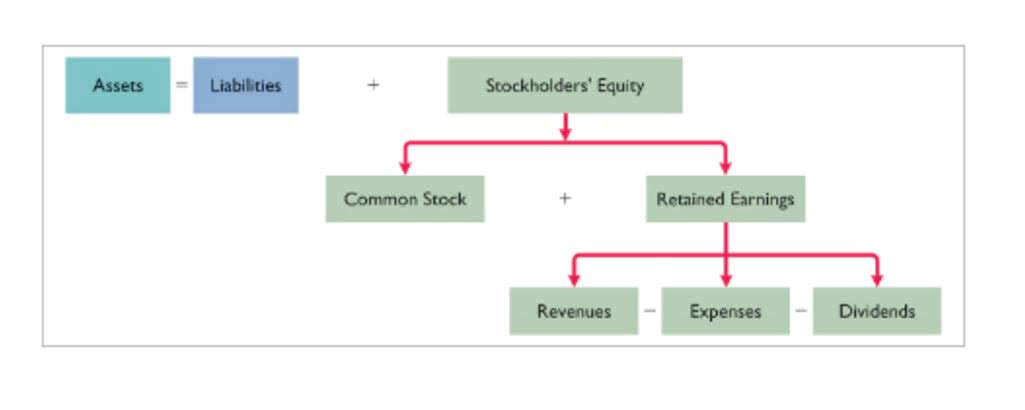
- In a cost graph, mixed costs are represented by a line that starts from a point on the y-axis (representing the fixed cost) and slopes upward, reflecting the variable component.
- From there, management tools are implemented to monitor and reduce the cost per unit made.
- One way to deal with a curvilinear cost pattern is to assume a linear relationship between costs and volume within some relevant range.
- Mixed costs refer to a combination of both a fixed and variable component.
- At CoCountant, we help you analyze and manage mixed costs to boost profitability and simplify budgeting.
Calculating Mixed Costs for Budgeting
In conclusion, mixed costs include both fixed and variable elements. Identifying the fixed and variable portions of a mixed cost is essential to make informed business decisions. Understanding cost behavior and using appropriate methods to separate fixed and variable costs is critical to managing costs effectively. As activity level increases, the total mixed cost increases, but at a different rate depending on the proportions of fixed and variable components. The fixed component remains unchanged, while the variable component increases proportionally with activity.

Service Industry
By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of mixed cost and its implications for businesses. In Canada, accounting standards such as the International Financial Reporting https://www.access2care.bt/how-are-accounts-in-the-general-ledger-numbered/ Standards (IFRS) and Accounting Standards for Private Enterprises (ASPE) provide guidelines for cost behavior analysis. Compliance with these standards ensures accurate financial reporting and enhances decision-making. On the other hand, the variable component will go up or down depending on the level of activity. The fixed component will relatively stay the same whatever the level of activity is.
Why is understanding mixed costs important?
While conceptually more complex, software tools readily perform regression analysis, providing a robust estimation of cost behavior. The fixed component of a mixed cost represents a baseline charge that a business incurs even with no activity, such as a base service fee for a utility connection or a fixed monthly bookkeeping for cleaning business rental. The variable component, conversely, changes based on the actual usage or volume of activity, like charges for each unit of electricity consumed or per-mile costs for vehicle operation.
